TUBERCULOSIS (TB)
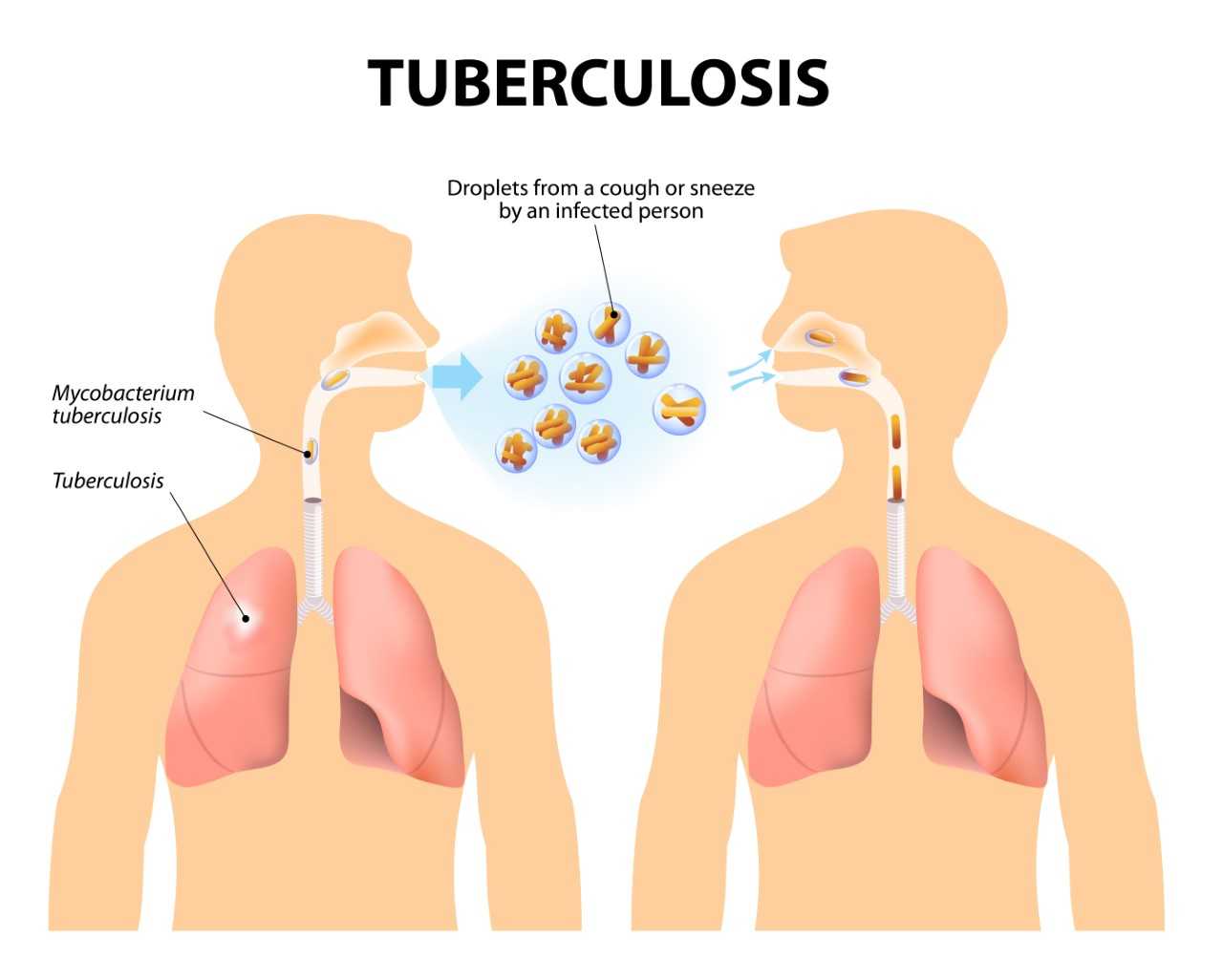
Tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious
airborne disease caused by Myco-bacterium tuberculosis, a bacterium that grows
and divides inside of cells. The infection, which starts in the lungs, causes
nodules known as tubercles, which are spots left by dead infected tissue. With
time, the disease can spread to other areas of the lung and larger areas of
lung tissue may die off, causing cavities. Bacteria can also spread to other
organs, including the kidney, brain, and spine.
Active TB typically
causes many symptoms that are most commonly related to the respiratory system,
including coughing up blood or sputum (phlegm). You may experience a cough that
lasts for over three weeks and pain when coughing or with normal breathing.
Other symptoms include:
• unexplained fatigue
• fever
• night sweats
• appetite loss
• weight loss
While TB usually affects
the lungs, it can also affect other organs, such as the kidneys, spine, bone
marrow, and brain. Symptoms will vary depending on which organ is infected. For
example, tuberculosis of the kidneys can cause you to urinate blood.
